
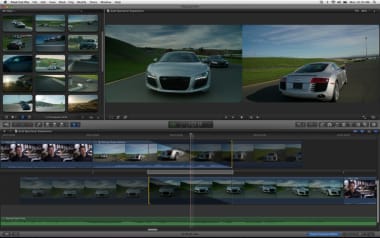
7.0.3 and earlier) Final Cut (Pro and Express) interface was designed around non-computerized editing workflows, with four main windows that replicate tried-and-trusted methods of organising, viewing and editing physical tape or film media. It also has multiple color correction tools including color wheels, sliders and curves, video scopes and a selection of generators, such as slugs, test cards, and noise. It comes with a range of video transitions and a range of video and audio filters such as keying tools, mattes and vocal de-poppers and de-essers.
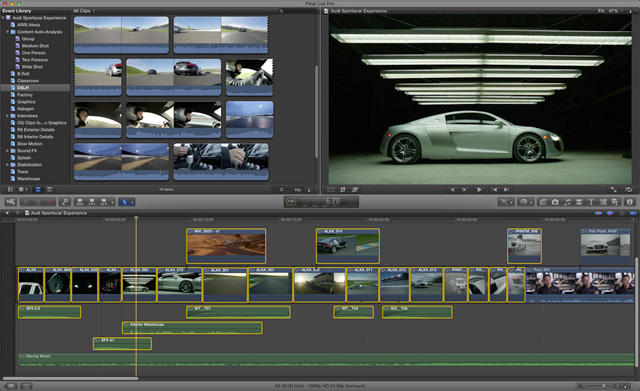
It supports a number of simultaneously composited video tracks (limited mainly by video form capability) unlimited audio tracks multi-camera editing for combining video from multiple camera sources 360º video editing support as well as the standard ripple, roll, slip, slide, scrub, razor blade and time remapping edit functions. 5 Major films edited with Final Cut Proįinal Cut Pro provides non-linear, non-destructive editing of any QuickTime-compatible video format including DV, HDV, P2 MXF (DVCProHD), XDCAM (via plug-in), 2K, 4K, 5K, and 8K film formats and can import projects directly from iMovie for iOS and iPadOS.A published survey in 2008 by the American Cinema Editors Guild placed their users at 21% Final Cut Pro (and growing from previous surveys of this group), while all others were on an Avid system of some kind. According to a 2007 SCRI study, Final Cut Pro made up 49% of the United States professional editing market, with Avid at 22%. It has also made inroads with film and television editors who have traditionally used Avid Technology's Media Composer. Since the early 2000s, Final Cut Pro has developed a large and expanding user base, mainly video hobbyists and independent filmmakers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
